PIMCO Makes Changes to BOND
Last week PIMCO announced changes (PDF) to its flagship Total Return active ETF, BOND. The gist: different investment focus to meet changing investor needs, new management team, same ticker.
I had a quick comment in the Ignites story (subscription required) on the change in which another observer stated that the appropriate move for PIMCO in this case is to launch another product, not tweak BOND. I find the move interesting enough that I thought to cover a few more things. So, three points each on two topics:
What’s Important About the Context Surrounding the Change?
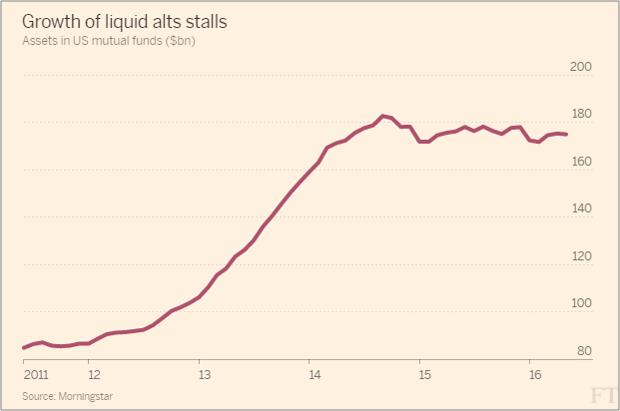
- BOND is roughly $2 billion in assets. Not to minimize those assets, but they’re small relative to the whole of the Total Return strategy (75B+ in the mutual fund alone) and the firm’s $1.5 trillion in AUM.
- In general, active ETFs have not taken off as some have hoped. It’s difficult to project that PIMCO’s changes to BOND put a significant short or mid-term influx of assets at risk.
- Positioning the move as being grounded in the changing needs of investors is (a) appealing given the nature of today’s bond market, and (b) credible given that PIMCO is altering a product that has performed well, not poorly.
So Why Might This be Worth Doing?
- The Total Return strategy has been on the defensive since the fallout from Bill Gross’s departure. At least for the ETF this move enables PIMCO to focus on client needs and the new (and strong) team as part of a more positive conversation.
- Transitioning an existing product avoids adding another active ETF into an already-crowded ETF market and one that (again) has not been overly conducive to active funds.
- The scale of the assets involved makes this a potentially-appealing learning exercise from a strategic standpoint. PIMCO can mine the implications of pivoting existing ETF offerings, recasting the messaging for Total Return, and the like. (I realize this is far-fetched but the move has me thinking about adopting the regular reinvention strategy of Chicago’s famous Next restaurant for an ETF.)
There are so many nuances to consider. Even the fact that the ticker symbol is unchanged has implications. After all, if people know only one thing about active ETFs, fixed income ETFs, and PIMCO ETFs, the BOND ticker is probably it. Will the ticker being the same undermine efforts to communicate the changes?
It will be interesting and fun to see how this ultimately plays out.