What Happens When Big Ideas are Worth Less?
Consider a hypothetical industry:
- Competition is intensifying.
- Organizations are investing heavily in analytical capabilities, both in terms of people and tools, in an attempt to find a new strategy that will give them an edge.
- Unfortunately for the innovators, new ideas and strategies are often quickly digested and leveraged by numerous competitors.
I happen to be talking about baseball, an industry so competitive these days that someone was just sent to prison for 4 years for hacking another team’s data. (Yes, with Spring Training starting I have a little too much baseball on my mind).
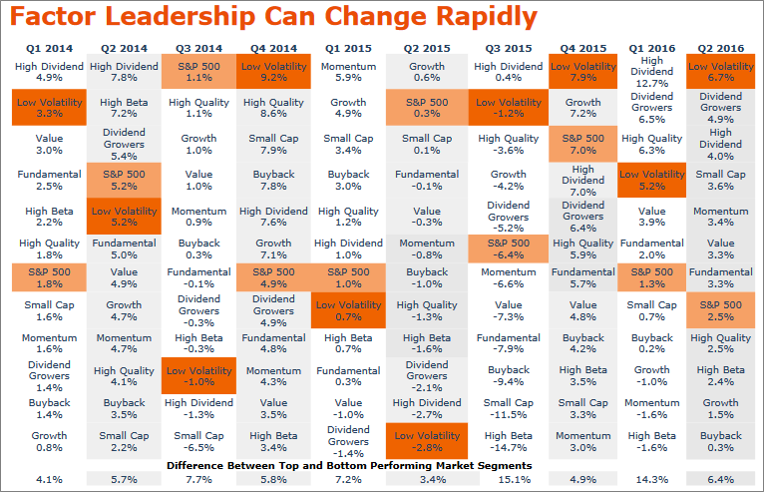
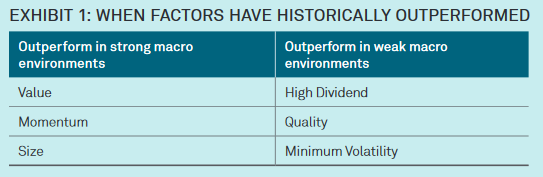
But the competitive realities in baseball – and their implications – parallel what is happening in asset management. Competition is rising. Firms continue to search for new business and distribution strategies in part by utilizing Big Data. And the window for firms to capitalize on new ideas is increasingly short.
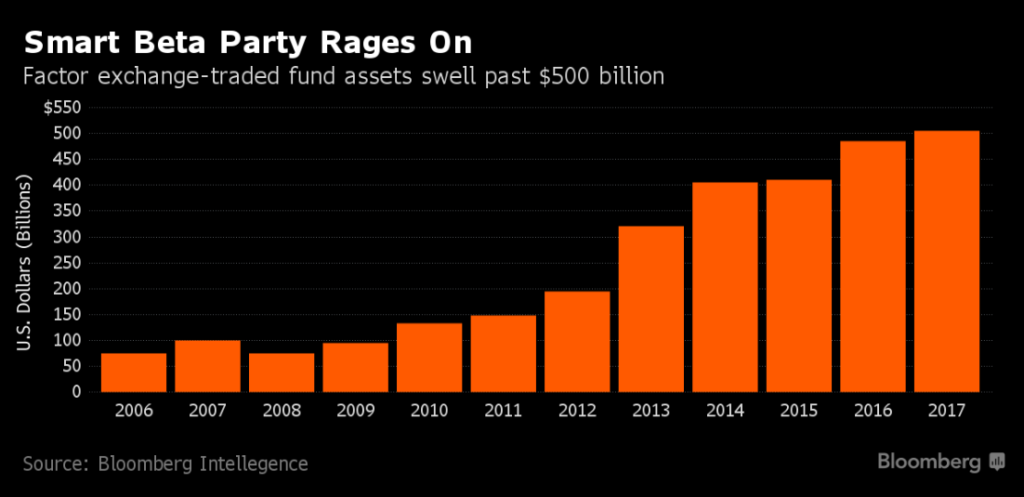
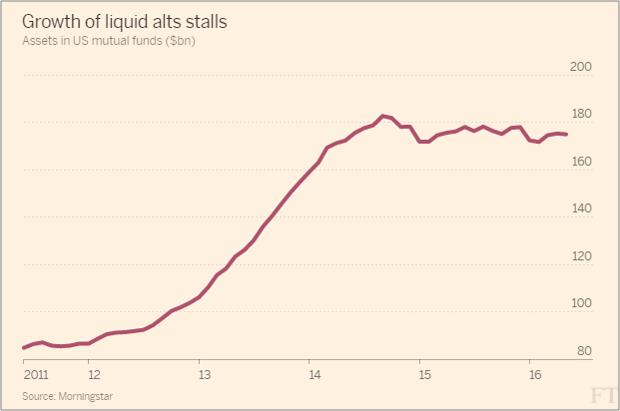
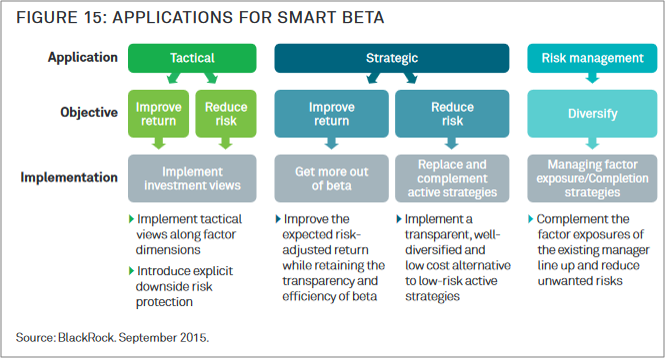
Smart beta provides a good example. Though the ideas have been around for a long time, for the most part firms did not perceive smart beta as a major opportunity until the last few years. Then, rapidly, there was a pivot. In short order the idea that smart beta is not just a niche but a potential core strategic effort for many firms took hold. Today it’s to the point where there are 800+ smart beta ETFs and mild concerns about it being a “market fad run amok.”
What does this mean for firms? What if your next new idea can be understood and cloned/tweaked by the competition almost immediately?
I think the first obvious step is simple acceptance that this will be reality moving forward. In the parallel baseball universe one writer called this “the devaluation of new ideas.” Firms need to accept that their big ideas are going to get out there faster than they’d like.
The second step is more critical. It involves firms placing a greater emphasis on execution over strategy. Coming up with the idea first matters less; implementing the idea as creatively, uniquely, and efficiently as possible becomes paramount.
While this is somewhat of a broad, abstract concept, I find the notion interesting in light of the varied effort we see invested in strategy definition and innovation across our clients. A shift in an organization or team’s fundamental mindset can have an important impact on approaches to everything from product development to distribution tactics.